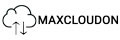When building or upgrading a PC, you might have faced the challenge of limited PCIe slots - especially if you want to connect multiple GPUs, NVMe SSDs, or other high-speed expansion cards. This limitation also applies if you need a higher PCI-E device count. That’s where PCIe lane splitting comes in.
At MaxCloudON, we first came across bifurcation when we were looking for a way to maximize the GPU count for the servers used in our data centers. At that time (around 2010-2011) the only possible way to build a multi-GPU server was by using proprietary and highly-expensive PCIe switches. After extensive research and testing different setups, we realized how important GPU bifurcation would be for us in offering multi-GPU servers without relying on proprietary PCI-E switches.
In this guide, I’ll explore what PCIe bifurcation is, how it works, which motherboards support it, and how to enable it in BIOS. This guide is based on our extensive observations and tests over the years, and the conclusions we have drawn from our own experience. We’ll also compare PCIe switches vs. bifurcation, discuss multi-GPU setups, and share insights on using bifurcation risers and adapters.
Whether you're an enthusiast looking to optimize your system or a professional needing a reliable multi-device setup, this post will help you understand and implement PCIe bifurcation effectively.
What is PCIe Bifurcation?
Definition and Basic Explanation
Bifurcation PCIe is the logical division of a single PCI Express (PCIe) slot into multiple independent slots, allowing multiple devices to share a single PCIe connector. This is particularly useful for users who need to expand PCIe slots.
Instead of using one device per slot, bifurcation enables multiple devices - such as GPUs, NVMe SSDs, or network cards - to operate simultaneously within a single physical slot by dividing its available lanes into separate logical pathways.
Based on our experience, we first noticed bifurcation as an active setting in different servers using LGA2011 platforms – one of the first platforms to support numerous PCIe express lanes and enable advanced PCIe configuration. For quite some time, we wondered what this feature was, and eventually, we took a deep dive into it and prototyped our first PCIe 3.0 riser.
At first, going beyond the PCIe specification was a bit challenging, but after testing different wiring alloys, connectors, solder materials, and production techniques we successfully developed our first working riser. This riser featured a 60 cm cable length and supported PCIe 3.0 bifurcation in an x4x4x4x4 mode.
Why is PCIe Bifurcation Important?
PCIe bifurcation is essential for advanced computing, server, and workstation builds, where high PCIe bandwidth output is required. As it turned out later, gaming rigs and desktop builds could benefit from bifurcation, especially when maximizing PCIe connectivity is crucial.
The key roles of our bifurcated risers include, but are not limited to:
- Multi-GPU Configurations: Enables multiple GPUs in a single slot for applications like AI, machine learning, and 3D rendering. If you're looking for pre-configured, high-efficiency GPU servers, explore our Dedicated GPU Servers.
- NVMe SSD Expansion: Allows multiple NVMe SSDs – both M.2 and server grade U.2 - to connect through a single PCIe slot, improving storage performance and capacity.
- Optimized PCIe Lane Distribution: Efficiently utilizes motherboard PCIe slots without expensive PCIe switches or additional expansion cards.
How Does PCIe Bifurcation Work?
PCIe Lanes Explained
A PCIe slot operates using “lanes”, acting as high-speed data highways between the CPU (or PCI-E controller) and connected devices. These lanes come in different configurations: x1, x4, x8, and x16, indicating the number of available lanes for data transfer.
A PCIe slot is bifurcated when its lanes are divided among multiple devices. For example:
- A PCIe x16 slot can be bifurcated into x8/x8 (splitting into two x8 slots) or x4/x4/x4/x4 (splitting into four x4 slots). On some mostly server motherboards, x8x4x4 or x4x4x8 are available.
- A PCIe x8 slot can be split into x4/x4.
Hardware and BIOS Dependency
PCIe bifurcation is not a plug-and-play feature; it requires support from the motherboard's BIOS/UEFI firmware and the chipset. Some motherboards allow users to manually configure bifurcation settings, while others require specific riser cards or adapters to function properly.
At MaxCloudON, we rely on manual configuration. That said, to use our PCIe bifurcated risers, you will need to enable active bifurcation in BIOS settings.
Key Factors That Affect PCIe Bifurcation:
- Motherboard Compatibility: Not all motherboards support bifurcation - high-end overclocking and workstation motherboards are more likely to offer this feature. Always check whether your motherboard BIOS settings have active bifurcation. If you are unsure contact our support team to check compatibility.
- Chipset Limitations: Intel and AMD chipsets differ in their PCIe expansion capabilities.
- BIOS Settings: Users need to enable bifurcation in the motherboard’s BIOS for proper functionality. As of this guide’s publication, our risers support up to PCIe Gen 3.0, making it essential to enable this option for compatibility.
Motherboard and Chipset Compatibility for PCIe Bifurcation
Which Motherboards Support PCIe Bifurcation?
Not all motherboards support bifurcation, but many high-end and workstation models include this feature. We have found HEDT motherboards that do NOT support bifurcation and budget models that DO. The price tag isn’t always a guarantee. Here are some examples:
PCIe Bifurcation Motherboard List:
Consumer Motherboards (Gaming & Enthusiast)
- ASUS ROG and TUF series
- MSI MEG and MPG series
- Gigabyte AORUS and Ultra Durable series
- ASRock Taichi and Phantom series
- EVGA FTW and Dark series
These motherboards often support bifurcation for multi-GPU setups, NVMe storage expansion, and other resource-intensive applications. However, we have observed some inconsistencies in Asus and MSI motherboards - for example, certain slots may function exclusively as m2 slots.
Workstation & Server Motherboards
For professional workloads, many workstations and server-grade motherboards provide extensive bifurcation support. These include:
- ASUS Pro WS series
- Supermicro X12 and X13 series
- Gigabyte WRX80 series (for AMD Threadripper Pro)
- ASRock Rack motherboards
Chipsets with PCIe Bifurcation Support
The chipset is a key factor in determining PCIe bifurcation compatibility. Below are some chipsets known to support this feature.
Intel Chipsets:
- Z490, Z590, Z690, Z790 – Found in high-end consumer motherboards.
- X299, C621, C622 – Workstation and server chipsets with extensive PCIe lane support.
- W680, C422 – Business and professional workstation motherboards.
AMD Chipsets:
- X570, B550 (limited support) – Consumer and enthusiast-grade motherboards.
- TRX40 – Designed for AMD Threadripper with multi-GPU and NVMe bifurcation support.
- WRX80 – Workstation-grade chipset supporting versatile PCIe configurations.
Remember that a motherboard's price range doesn’t always guarantee PCIe bifurcation support. So always verify compatibility before purchasing.
How to Check if Your Motherboard Supports PCIe Bifurcation:
- Look at the motherboard's manual or manufacturer’s website.
- Check the BIOS settings under Advanced PCIe Configuration. If your motherboard supports bifurcation, you can enhance your setup with a PCIe x16 to 2x8 Bifurcation Riser or a Bifurcated riser x16 to 4x4 Set.
- Search for online forums or manufacturer FAQs discussing bifurcation support for your specific model.
If your motherboard supports bifurcation, you can configure it in the BIOS. In the next sections, we will cover how to enable and use PCIe bifurcation, along with practical applications such as multi-GPU setups and NVMe storage expansion.
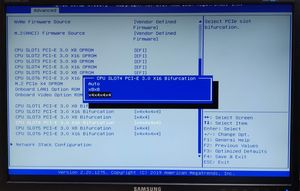
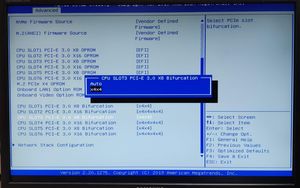
How to Enable and Use PCIe Bifurcation (Step-by-Step Guide)
If your motherboard supports PCIe bifurcation, you have to enable it manually in the BIOS. Follow these steps:
Step 1: Check Your Motherboard’s Support
Before proceeding, verify that your motherboard supports PCIe bifurcation by checking:
- The motherboard manual or manufacturer’s website.
- Online forums where users discuss specific BIOS settings for bifurcation.
- The BIOS settings under Advanced PCIe Configuration.
Step 2: Enter BIOS/UEFI
- Restart your computer and enter the BIOS by pressing DEL, F2, or another key (varies by manufacturer).
- Navigate to the Advanced Settings or PCIe Configuration section.
Step 3: Locate Bifurcation Settings
- Look for a setting labeled PCIe Slot Configuration, Bifurcation Mode, or something similar.
- Some BIOS menus may list it under Advanced > PCI Subsystem Settings.
Step 4: Enable the Desired Bifurcation Mode
- Choose the appropriate bifurcation setting based on your hardware:
- x8/x8 (for dual-GPU or dual NVMe setups).
- x4/x4/x4/x4 (for four NVMe SSDs, GPU and other expansion cards).
- Other available configurations depending on your motherboard.
Step 5: Save Changes and Exit
- After selecting the appropriate bifurcation mode, save the changes and exit the BIOS.
- Restart your system and verify device detection in Windows, Linux, or macOS.
PCIe x16 Bifurcation: What It Means and How It Works
What is PCIe x16 Bifurcation?
- PCIe x16 bifurcation refers to splitting a single x16 PCIe slot into multiple smaller PCIe slots.
- This is useful for connecting multiple GPUs, NVMe SSDs, or expansion cards without adding additional physical slots.
Common Bifurcation Modes for PCIe x16 Slots
A standard PCIe x16 slot can be bifurcated into:
| Bifurcation Mode | Configuration | Use Case |
| x8/x8 | 2x8 slots | Dual GPU setup, NVMe SSDs |
| x4/x4/x4/x4 | 4x4 slots | NVMe RAID, multi-device setups |
| x8/x4/x4 | 1x8 and 2x4 slots | Mixed GPU and SSD configuration |
Why Use PCIe x16 Bifurcation?
- Multi-GPU setups for machine learning, AI, or rendering.
- NVMe storage arrays for RAID configurations.
- Maximizing motherboard PCIe expansion without needing a PCIe switch.
Limitations of PCIe x16 Bifurcation
- Performance Impact: Some GPUs may experience reduced bandwidth when operating in x8 or x4 mode; however, based on our observation this is rarely the case. In 99.9% of the cases, x8 at PCI-E 3.0 is sufficient to fully utilize a modern GPU, and x4 at PCIe 3.0 is sufficient in 98% of cases;
- Motherboard Restrictions: Not all consumer-grade motherboards allow full bifurcation.
- BIOS Configuration Required: Bifurcation must be enabled manually on most motherboards.
PCIe Bifurcation for GPU: Multi-GPU Setups Explained
Can You Use PCIe Bifurcation for GPUs?
Yes, the bifurcation option allows you to run multiple GPUs in a single PCIe slot. However, there are some limitations to consider.
Best Use Cases for Multi-GPU Bifurcation
- Machine Learning & AI Workloads – Training deep learning models with multiple GPUs.
- 3D Rendering & CAD – Running GPU-intensive applications like Blender, Octane, and V-Ray.
- Mining Rigs – Using multiple GPUs for cryptocurrency mining.
- Gaming (Limited Use) – While most modern GPUs operate efficiently in x8 mode, running a high-end GPU in x4 mode may cause noticeable performance loss.
Performance Considerations for Bifurcated GPUs
| Configuration | Suitable for Gaming? | Suitable for AI/Rendering? |
| x16 (full bandwidth) | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| x8/x8 (dual GPUs) | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| x4/x4/x4/x4 (four GPUs) | ✅ Yes (minor bottleneck) | ✅ Yes |
How to Optimize Multi-GPU Performance in a Bifurcated Setup
- Use GPUs that perform well in x8 mode, such as NVIDIA RTX 3090/4090/5090 or AMD Radeon RX 7900 XTX.
- Ensure your motherboard has enough PCIe lanes to support bifurcation.
- Use PCIe risers or bifurcation adapters if necessary.
- Enable Resizable BAR. To use MaxCloudON’s bifurcation risers, PCIe Gen3 support must be manually enabled. Failure to do so will result in major dysfunctionality of your GPU.
PCIe Switch vs. Bifurcation: Key Differences and Use Cases
What is a PCIe Switch?
A PCIe switch is a hardware component that manages multiple PCIe devices by dynamically distributing PCIe lanes. Unlike PCIe bifurcation, which simply splits available lanes at the motherboard level, a PCIe switch allows for lane aggregation, prioritization, and dynamic allocation of PCIe bandwidth.
What is PCIe Bifurcation?
This BIOS-based method splits PCIe lanes into separate logical connections without requiring additional hardware. It depends on motherboard support and is commonly used for running multiple GPUs or NVMe SSDs from a single PCIe slot.
Comparison: PCIe Switch vs. PCIe Bifurcation
| Feature | PCIe Bifurcation | PCIe Switch |
| Definition | Splits PCIe lanes at the motherboard level | Uses a dedicated chip to manage PCIe traffic. |
| Requires BIOS Support? | Yes | No |
| Flexibility | Limited to predefined BIOS configurations | Can dynamically allocate lanes and bandwidth |
| Use Cases | Multi-GPU, NVMe RAID, storage expansion | Enterprise servers, high-speed networking, PCIe expansion |
| Cost | Low (explore MaxCloudON risers). | High (requires a PCIe switch card or motherboard integration). |
When to Use PCIe Bifurcation vs. PCIe Switch
Use PCIe Bifurcation if:
- Your motherboard supports it.
- You need a cost-effective way to add multiple NVMe SSDs or GPUs.
- You don’t need dynamic bandwidth management.
Use a PCIe Switch if:
- You need more PCIe lanes than your CPU/motherboard provides.
- You require load balancing across multiple PCIe devices.
- You're working with high-performance computing (HPC) and enterprise solutions
Why Use PCIe Bifurcation? Best Use Cases
Why Should You Use Bifurcation PCIe?
It is an efficient way to maximize your system’s PCIe slot utilization without needing additional PCIe switches. Whether you're building a high-end workstation, upgrading a gaming PC, or optimizing a server, bifurcation can provide significant benefits.
Top Use Cases for PCIe Bifurcation
1. Multi-GPU Setups for AI & Machine Learning
- PCIe bifurcation allows multiple GPUs to be used for deep learning and AI training.
- Workstations and servers benefit from parallel computing without requiring additional PCIe slots.
2. NVMe Storage Expansion & RAID Configurations
- Many motherboards support PCIe x16 to 4x M.2 adapters, allowing four NVMe SSDs in a single slot.
- Ideal for high-speed RAID 0, RAID 1, or RAID 5 configurations.
3. High-end Workstations & 3D Rendering
- VFX artists, architects, and game developers use bifurcated setups for GPU rendering.
- Rendering engines like Blender, Octane Render, and V-Ray leverage multiple GPUs efficiently.
4. Home Servers and NAS Systems
- PCIe bifurcation enables additional network cards, SSD storage, and RAID controllers in home lab environments.
- Works well for TrueNAS, Unraid, and Proxmox-based setups.
5. Cryptocurrency Mining
- Mining rigs often use bifurcation risers to split a PCIe slot into multiple x1 or x4 connections.
- Helps miners connect multiple GPUs for crypto mining. We have developed a special board for this, where it can be used with already existing mining hardware.
Of course, these don’t fully cover all the possible uses of PCIe bifurcation. Since PCI-e bifurcation effectively "creates" additional PCI-e slots, there are various use cases. For example, we have seen people build mixed servers for NAS and video surveillance.
Future Development of MaxCloudON PCIe Risers
By far, MaxCloudON is a data center provider, who hosts its own servers in its own data centers and offers them to various companies and freelances for advanced computing needs. Initially developed for in-house use, we decided to develop our PCI-e risers as standalone products and make them available to a wider audience.
To address the multiple inquires regarding when we will develop PCI-E Gen 4.0, 5.0 and 6.0 risers, we clarify that these generations have already been approved as technical specifications. However, our development strategy aligns with our core business needs. We have not yet developed PCIe Gen 4.0 risers simply because we have not found them necessary - PCIe 3.0 fulfills 99% of our use cases.
Another significant concern regarding PCIe bifurcation risers for PCIe 4.0, 5.0, and 6.0 is the price factor. Our development team has explored these options, and we are somewhat cautious about how the market would react to their pricing. Preliminary estimates suggest that even if we develop such a riser, its price could be 100-150% higher than PCIe 3.0 pricing.
This price increase is primarily due to higher frequencies in PCIe 4.0 and above, which require redrivers/retimers to enhance signal integrity. Additionally, the new materials needed to manufacture these risers would be significantly more expensive than those used in PCIe Gen 3.0.
Final Thoughts
PCIe bifurcation is a powerful feature that allows multiple GPUs, NVMe SSDs, and other PCIe devices to share a single PCIe slot efficiently. Whether you are a gamer, content creator, AI researcher, or system builder, bifurcation provides an affordable and scalable way to expand PCIe connectivity.
Need a PCIe bifurcation riser or adapter? Check out our online shop for high-quality bifurcated risers, PCIe adapters, and more!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About PCIe Bifurcation:
1. Can I enable PCIe bifurcation on any motherboard?
No, only motherboards with BIOS support for PCIe bifurcation can enable it. High-end gaming, workstation, and server motherboards are more likely to include this feature.
2. Does PCIe bifurcation reduce performance?
It depends on the workload:
- For GPUs, running in x8 mode instead of x16 mode usually has minimal impact.
- For NVMe SSDs, there is no performance loss if lanes are properly allocated.
3. Can I use PCIe bifurcation for gaming?
Yes, but with limitations:
- A single GPU running in PCIe x8 mode will perform almost the same as x16 mode.
- Running a high-end GPU in x4 mode may cause mild bottleneck in some gaming situations.
4. Do all CPUs support PCIe bifurcation?
No. The CPU must support lane splitting. High-end Intel & AMD CPUs (like Intel Core i9, AMD Ryzen 9, Threadripper) usually support bifurcation. Budget CPUs may not offer enough lanes for proper bifurcation. Still, always check with your CPU/motherboard model.
5. Can I enable PCIe bifurcation without BIOS support?
No. If the motherboard’s BIOS does not support PCIe bifurcation, you cannot enable it manually. However, you can use a PCIe switch card, which does not require BIOS support.
6. Do I need a special riser for PCIe bifurcation?
Yes, a PCIe bifurcation riser is required to connect multiple devices.
7. Is PCIe bifurcation useful for server builds?
Yes! Many server motherboards support PCIe bifurcation for:
- Expanding NVMe storage.
- Running high-speed network adapters.
- Adding multiple RAID controllers.